Loading Audio Signal¶
We recommend using modusa.io.AudioLoader to create modusa.signals.AudioSignal instance.
[44]:
from modusa.io import AudioLoader
Audio can be loaded from different sources. You can load audio from file, np.array, YouTube, etc.
From local audio file¶
[46]:
# From file path
audio_from_fp = AudioLoader.from_fp(
"../../../../../music/songs/song.mp3")
audio_from_fp.print_info() # Use this to print the details of the audio
--------------------------------------------------
Title : song.mp3
Kind : Audio Signal
Duration : 153.47 sec
Sampling Rate : 48000 Hz
Sampling Period : 0.0208 ms
--------------------------------------------------
From YouTube¶
Incase, you have your your own video content hosted on YouTube, you can directly load it as an audio signal.
[31]:
# From YouTube
audio_from_youtube = AudioLoader.from_youtube(
url="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lIpw9-Y_N0g",
sr=None) # None to keep it at source sampling rate
audio_from_youtube.print_info()
display(audio_from_youtube.play(regions=[(0, 10), (40, 55)]))
--------------------------------------------------
Title : Ankit Anand Music - Tu Hi Bta (तू ही बता) [Official Lyrical Video] || Feat. Liza Joshi
Kind : Audio Signal
Duration : 242.42 sec
Sampling Rate : 48000 Hz
Sampling Period : 0.0208 ms
--------------------------------------------------
Ankit Anand Music - Tu Hi Bta (तू ही बता) [Official Lyrical Video] || Feat. Liza Joshi
If you already have the audio signal loaded in np.array
and want to create an
modusa.signals.AudioSignal instance from it.Here is how you can do that.
[47]:
import librosa
x, sr = librosa.load(
"../../../../../music/songs/song.mp3",
sr=None)
audio_from_array = AudioLoader.from_array(
y=x,
sr=sr)
audio_from_array.title = "song.mp3 (Loaded from an array)"
audio_from_array.print_info()
--------------------------------------------------
Title : song.mp3 (Loaded from an array)
Kind : Audio Signal
Duration : 153.47 sec
Sampling Rate : 48000 Hz
Sampling Period : 0.0208 ms
--------------------------------------------------
Generating Audio Waveforms¶
[33]:
# We have an AudioWaveformGenerator class with static methods
# to generate various audio waveforms
from modusa.generators import AudioWaveformGenerator
[34]:
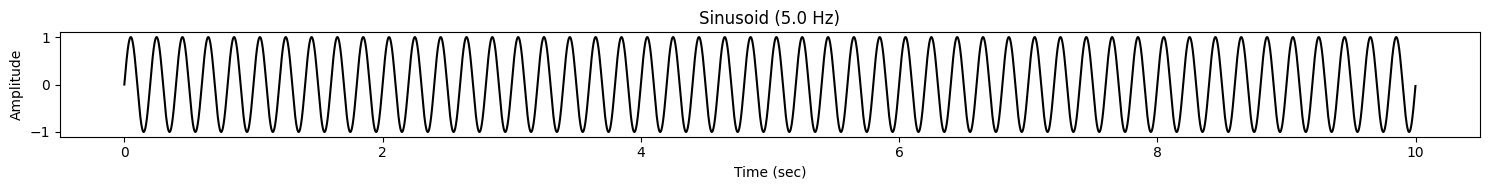
signal1 = AudioWaveformGenerator.generate_sinusoid(
A=1, f=5, phi=0, sr=1000, duration=10
)
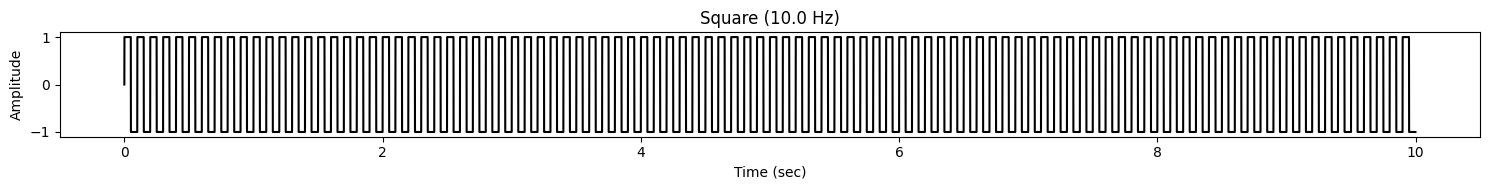
signal2 = AudioWaveformGenerator.generate_square(
A=1, f=10, phi=0, sr=1000, duration=10
)
[35]:
# We can use plot method available for
# all kinds of modusa signals
display(signal1.plot())
display(signal2.plot())
[36]:
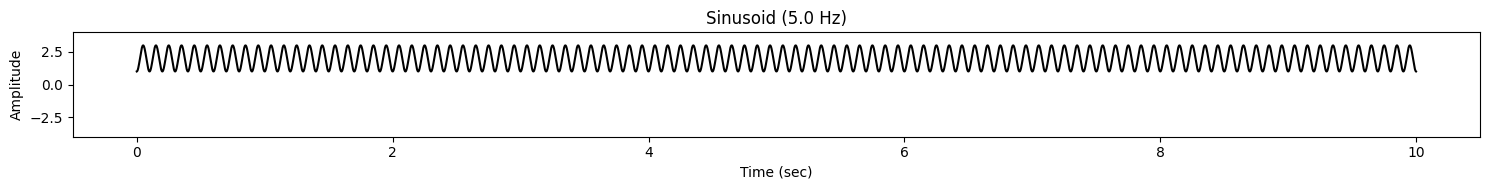
#------------------------------
# Basic aritmetic with scalar
# (Any arithmetic operation will be done element-wise,
# no change in the time index)
#------------------------------
signal = 2 * (signal1 ** 2) + 1
signal.plot(ylim=(-4, 4))
[36]:
[37]:
#------------------------------
# Signal to scalar transformation
# (Return float)
#------------------------------
signal1.max(), signal1.mean(), signal1.min(), signal1.std()
[37]:
(np.float64(1.0),
np.float64(2.6290081223123708e-17),
np.float64(-1.0),
np.float64(0.7071067811865476))
[38]:
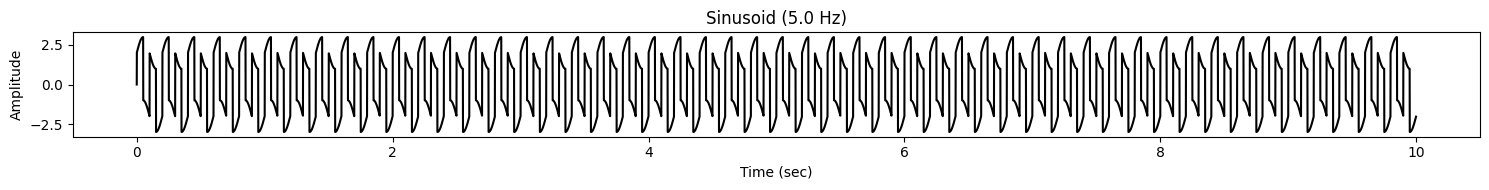
#------------------------------
# Signal and Signal operations
# (Returns another signal, the shape of the signals
# should be numpy compatible to perform operations)
#------------------------------
signal = signal1 + 2 * signal2
signal.plot()
[38]:
[39]:
#------------------------------
# Transformations like sin, cos, ...
# If there are operations that are not yet available,
# please let us know to implement those operations.
# While performing `np.` methods
# please verify if the behavior is as expected.
#------------------------------
signal = (1.1 + signal2).log()
signal.plot()
[39]:
[40]:
#------------------------------
# modusa signals are numpy compatible which
# mean you can apply np operations directy on
# them and still get signal object.
# However, there should be a wrapper for most
# common numpy operations, so you should first
# try use that.
#------------------------------
import numpy as np
np.abs(signal)
[40]:
Signal([0.09531, 0.7419, 0.7419, ..., 2.303, 2.303, 2.303], shape=(10000,), kind=AudioSignal)
[41]:
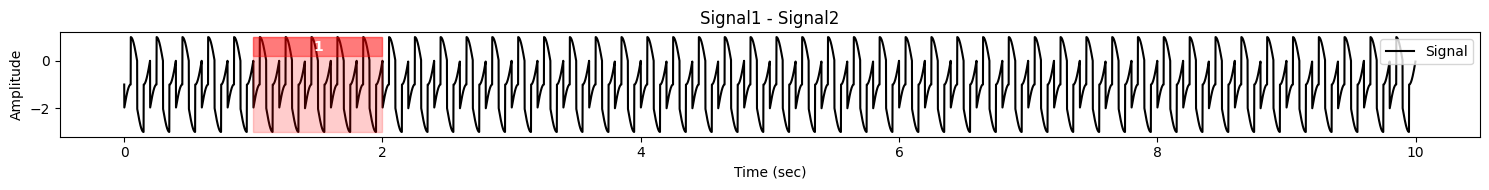
signal = (-1 + (signal1 - signal2))
signal.title = "Signal1 - Signal2"
signal.plot(highlight=[(1, 2)], label="Signal")
[41]:
[42]:
signal.play(regions=[(1, 5)])
Signal1 - Signal2
[42]:
[43]:
signal.print_info()
--------------------------------------------------
Title : Signal1 - Signal2
Kind : Audio Signal
Duration : 10.00 sec
Sampling Rate : 1000 Hz
Sampling Period : 1.0000 ms
--------------------------------------------------